
- 2 minutes to read
- 30 July 2019
Inhalation therapy is a standard treatment for acute or chronic conditions of the respiratory tract. By inhalation therapy, we mean the therapeutic inhaling of medication or the therapeutic moistening of the mucous membrane of the respiratory tract. The latter stimulates the self-cleaning mechanism of the lungs. Semi-fluid secretion can thus be liquefied and therefore mobilised more easily. Additionally, the lungs are optimally ventilated since the inhalation process supports a more conscious and deeper breathing.
It is important to apply the therapy correctly. If not, the medication may not reach the intended location where it is supposed to have an effect. Most drugs need to enter the lungs deeply in order to take effect locally in the bronchi or be absorbed through the pulmonary alveoli into the blood.
However, not only the inhalation technology but also the size of the drops plays an essential role. Inhaling only water vapour (chamomile bath, etc.) is only meant for moistening the upper airways (nasopharyngeal cavity). The lower airways, such as the trachea or bronchi, cannot however be reached.
For deep inhalation, nebulising systems and metered-dose inhalers are available. The metered-dose inhalers are used exclusively for applying medication. Nebulising systems are used to moisten the respiratory tract.
For inhaling, a nebuliser and an inhalation set with a mask or a mouthpiece are needed. In the case of a tracheal tube, the inhalation set can also be connected directly to the catheter mount1.

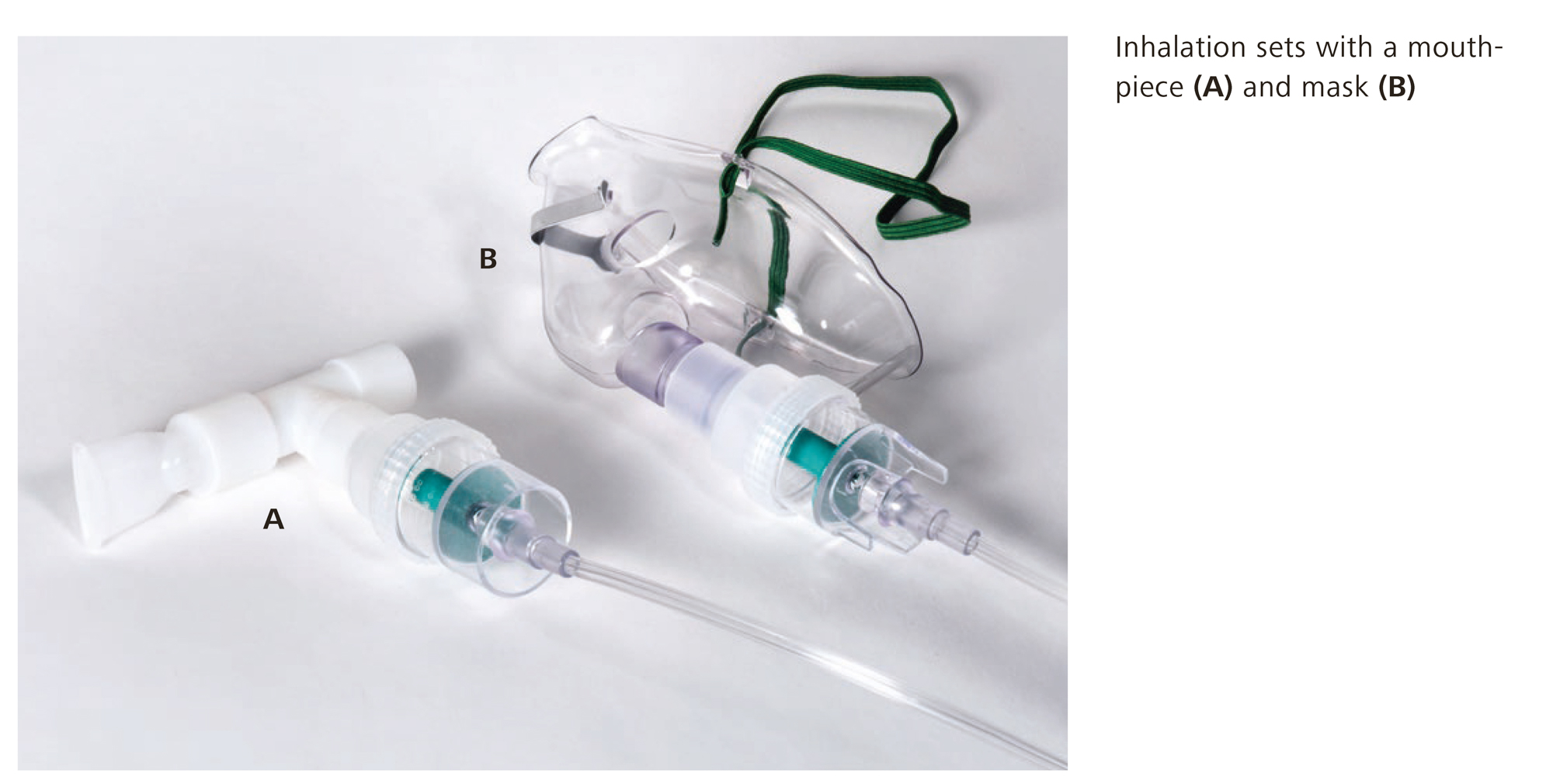
What is the right way to inhale?
- If possible, inhaling should be done in a sitting position to better expand the lungs
- Concentrating on calm and deep breathing
- After inhaling, possibly taking measures for mobilising secretion (e.g. expectoration with manual support or with Cough Assist)
- Watching order and time between individual inhalations in order not to reduce their effects
Which medication to inhale
- Bronchodilators
- Anti-inflammatory drugs (cortisone)
- Expectorant drugs (secretolytic drugs)
- Antibiotics
When using a mask for inhaling, it is important that it fits well since this can otherwise cause eye irritation or theimproper inhalation of the medication.
Cleaning
After each use, the inhalation set needs to be rinsed under running water. It needs to be stored in a dry place, e.g. in a cotton bag, and is replaced once per week.
After using drugs that contain cortisone, the mouth needs to be cleaned (e.g. by rinsing your mouth and throat, eating something or brushing your teeth) in order to get rid of the drug residue and to avoid fungal infestation in the mouth / throat area.
1 Tube extension

Be the first to comment!