What are the benefits for people with spinal cord injury?
- 3 minutes to read
- 23 May 2020
- Simea_
What are the benefits for people with spinal cord injury?
People with a spinal cord injury often suffer from spasticity and restrictions of movement. Can aquatic therapy achieve progress that cannot be achieved on land?
Common treatment methods for contractures and spasticity are:
- Physiotherapy
- Medication
- Active movement
- Warm, cold
- Electric stimulation
- Surgical interventions (orthopedic or neurosurgical).
A special form of physiotherapy is aquatic therapy. It may help improve spasticity and reduce the necessary amount of medication.
The advantages of water
- If submerged to the shoulders, the body weight is only approximately one tenth due to buoyancy and thus the pressure on the joints is reduced. Furthermore, movements can be carried out more easily that would otherwise be difficult or impossible to do outside of the water.
- Water pressure has a positive effect on blood circulation, metabolism, and respiration. It supports the recirculation of blood and lymphatic fluid toward the heart. Water resistance further stimulates the respiratory organs.
- The water streaming by relaxes the muscles through the skin receptors.
- Water resistance reduces the risk of falling. Due to a prolonged reaction time, balance issues can be corrected more easily. If the balance is lost after all, the fall is slower.

Important information in advance
It is recommended to perform aquatic therapy with a physiotherapist to determine an individual program and for safety reasons in the water. This also allows to discuss options in case of incontinence or open wounds.
A prerequisite to perform the following exercises is enough stability to be able to maintain an upright position in the water. This position can be taken sitting - or, if walking is possible – standing. Also, whether the exercises can be carried out exactly as described depends on the level and degree of severity of the spinal cord injury. Intentionally no indications are given about water depth, sequence and number of repetitions since they differ depending on prerequisites and goals.
Examples for active exercises
Exercises for the torso

(Source: www.vibss.de)
Starting position:
- Sitting on a swim noodle or board
- Upper body is upright
Ending position:
- One or both arms stretched sideways
- Trying to maintain an upright position
Support exercise

Starting position:
- Sitting or standing, torso upright (may be leaned on pool edge)
- Water barbell in one or both hands beside hips
- Elbows stretched
Ending position:
- Let barbell float up until the elbow touches the water surface then use your strength to press the barbell down again
- Torso remains upright
Torso exercise combined with arm exercise
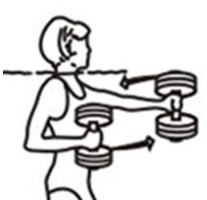
Starting position:
- Sitting or standing, torso upright (may be leaning on pool edge)
- Water barbell in one or both hands
- Arms under water, elbow on body
Ending position:
- Alternating stretch one arm out and retract
- When retracting, hold the barbell even tighter
- Torso remains upright
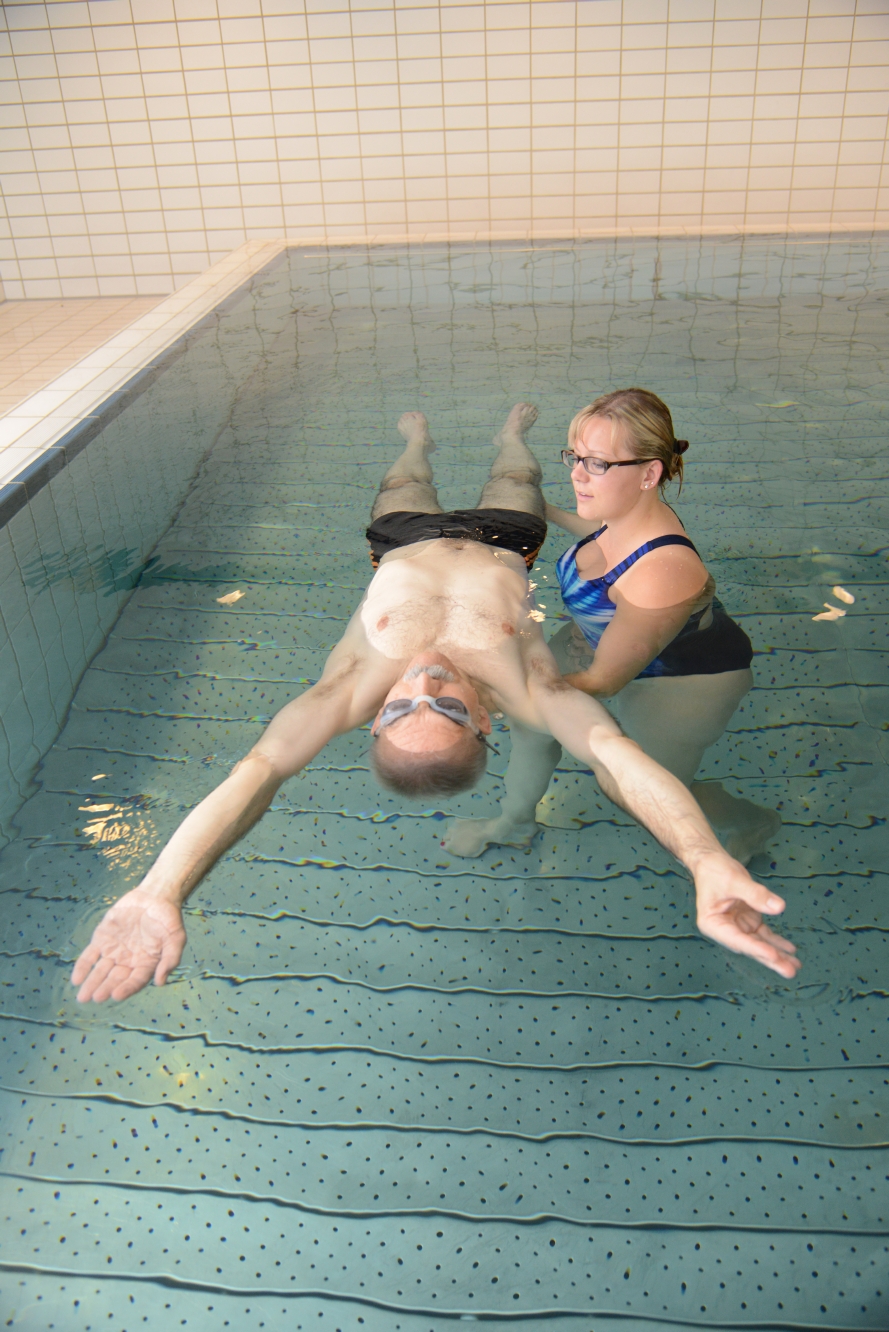
Backstroke

(Source: www.sichere-schule.de)
Starting position:
- On your back, therapist supports the back, possibly using the noodle as tool
- Arms beside hip
Ending position:
- One after the other, move stretched arms up over the head and bring back next to hips
- Hips remain on water surface

Water barbells
What else needs to be considered?
Not everyone enjoys water. Only those who enjoy water and go regularly will notice long-term results.
Choosing a suitable environment for aquatic therapy is essential, especially if using a wheelchair. Ideally, it is a pool that has a lift for transferring wheelchairs into the water. However, since only few public pools are wheelchair-accessible, flexibility may be required, for example when transferring into the water sitting on the floor. It should be clarified in advance whether the public pool is equipped with a folding shower chair or shower wheelchair.
The ideal water temperature differs for everyone. Therapy pools are usually a bit warmer in order to prevent undesired reactions such as an increase in spasticity.
Aquatic therapy may improve mobility, walking and spasticity. The characteristics of water provide a convenient environment for safe exercising.
Have you had any experiences with aquatic therapy? Or could you imagine trying it out?

